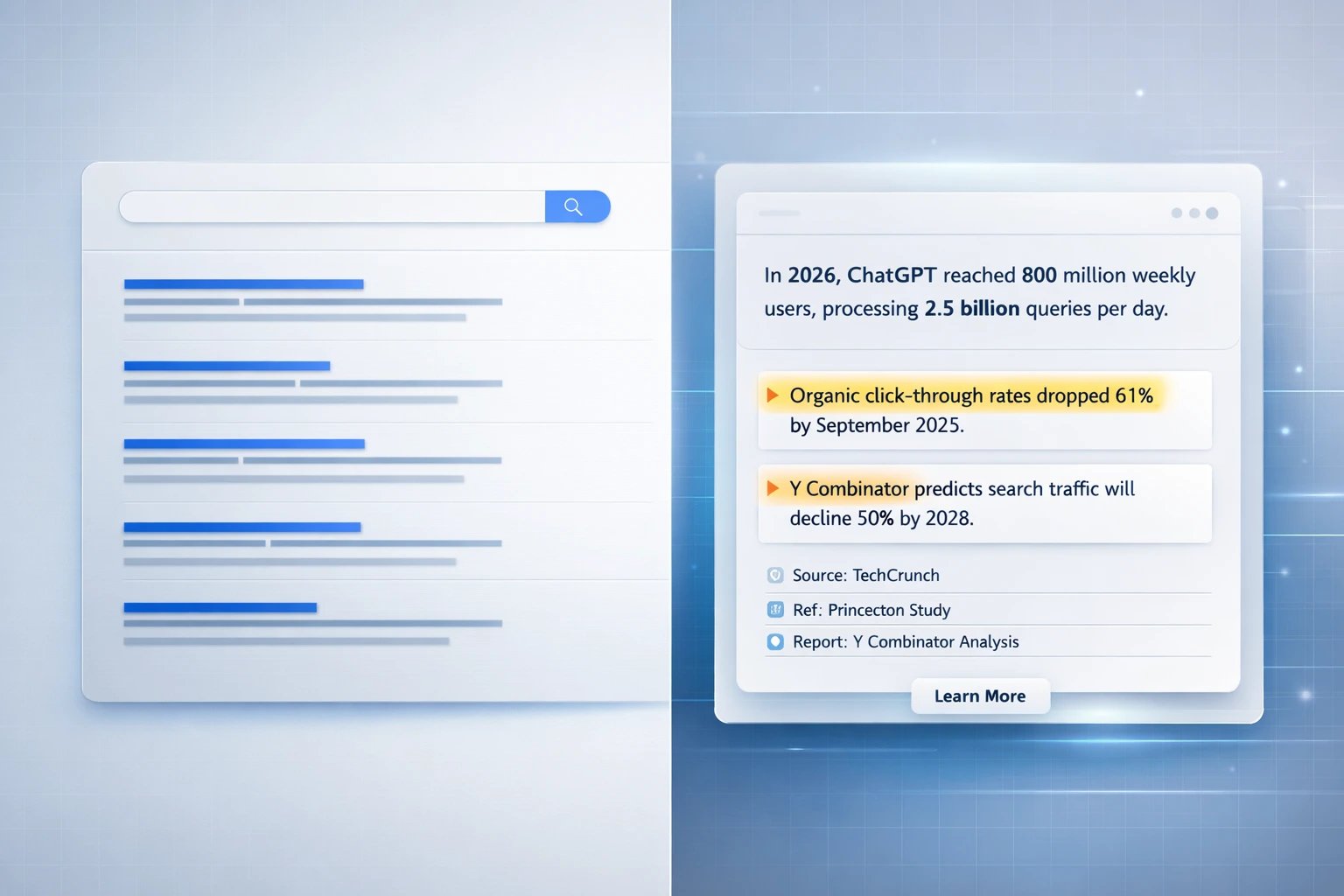
ChatGPT reached 800 million weekly users in October 2025, processing 2.5 billion queries daily as of July 2025. Perplexity hit 153 million monthly visits. These AI-driven search engines are fundamentally changing how people find information.
When AI-generated answers appear on Google, organic click-through rates dropped 61%, from 1.76% to 0.61% as of September 2025. Y Combinator projects traditional search traffic will decline 50% by 2028, with that volume migrating to generative engines..
What Is GEO and Why It Matters Now
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the practice of structuring content to increase citation probability in AI-generated responses. While traditional SEO focuses on search engine rankings, GEO optimizes for citation across ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, Claude, Gemini & other LLMs.
Research from Princeton, Georgia Tech, and the Allen Institute tested nine optimization methods across thousands of content samples:
Basic, unoptimized content scored 19.3 in visibility metrics. Adding authoritative citations, statistics, and improving content fluency increased visibility scores above 40, representing performance gains exceeding 100%.
The technical reason: AI systems use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). When a user asks a question, large language models retrieve relevant documents, evaluate them for authority and clarity, then synthesize a response. Content optimized for machine readability and credibility consistently outperforms content written solely for human readers.
Current adoption data shows 75% of digital agencies launched generative engine optimization services in 2025. The generative engine optimization market is projected to experience significant growth through 2030. Organizations that establish citation authority now benefit from compounding visibility as AI platforms favor sources they’ve previously cited.
How AI Search Differs From Traditional Search
Traditional search engines rank pages. AI engines synthesize answers. This creates different optimization requirements:
Source selection: Unlike traditional search engines LLMs cite a small number of highly relevant domains per response versus Google’s traditional 10 blue links. The inclusion threshold is higher.
Query interpretation: AI handles conversational queries. Users ask “What’s the best project management tool for remote teams under 20 people with Slack integration?” instead of “project management software.” This shift in search behavior requires different optimization approaches.
Content evaluation: AI prioritizes structured data, clear hierarchies, citations to authoritative sources, statistics over qualitative claims, and content answering specific user queries.
Traffic patterns: Significant portions of younger users now conduct searches through AI tools rather than traditional search engines. Growing numbers of consumers use AI for product recommendations. Zero-click searches represent the majority of Google queries.
Research-Backed GEO Strategies
Princeton GEO study findings on techniques that improve AI visibility:
Add quantitative statistics. Content with specific numbers instead of qualitative descriptions increased visibility 40%+. “Companies using this approach see 67% faster implementation” outperforms “Companies implement more quickly.” Law, government, and opinion-based content benefit most.
Include authoritative citations. Referencing credible sources increased visibility 31.4% when combined with other methods. Citations work for factual questions requiring verification. Link to research papers, government sources, industry reports, established publications.
Optimize fluency and readability. Improving sentence structure and clarity boosted visibility 15-30%. AI engines prioritize easily parsed content. Use clear topic sentences, logical flow, avoid complex syntax.
Use structured data. FAQ schema pages receive disproportionately more citations. Content with H2/H3 question headers increases extraction probability. JSON-LD markup helps AI understand structure and relationships.
Create answer-ready content. Content directly answering questions in the first 100 words performs significantly better in AI citations. Start with the answer, then provide supporting detail.
Build external authority. Sites with regular citations from published sources and institutional links are favored. AI tools evaluate domain authority across the web, not just your site. Guest posts, industry mentions, and media coverage contribute to citation probability. E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) principles from traditional SEO apply even more strongly in generative engine optimization.
Leverage co-citations without links. AI powered search engines track brand mentions regardless of whether they include clickable links. When your brand appears alongside established authorities in articles, research, and industry content, AI systems map these relationships to evaluate credibility. Co-occurrence patterns influence citation decisions even without traditional backlinks. Focus on earning brand mentions in authoritative contexts.
Best Lists Strategy. Ahrefs analysis of 26,283 ChatGPT source URLs found that “best X” blog lists represented 43.8% of all cited page types. When software companies were recommended by ChatGPT, 34% of responses included that company’s own comparison list as a source.
Among cited lists, 79.1% were updated in 2025, with 26% updated in the past two months. Brands positioned in the top third of third-party comparison lists showed higher ChatGPT citation rates than those in bottom thirds. For SaaS and service businesses, publishing regularly-updated comparison content where you transparently position your solution creates citation opportunities. Include direct links to alternatives, specific feature comparisons, and clear differentiation. Update quarterly to maintain relevance.
The most effective approach combines multiple strategies. Fluency optimization plus statistics addition outperformed single methods by 5.5% in testing.
Technical Implementation
Schema markup: Implement FAQ, HowTo, Organization and other relevant Schema using JSON-LD format. Schema markup enables AI engines to extract information with 300% higher accuracy compared to unstructured content. These machine-readable formats feed directly into AI retrieval systems.
Content hierarchy: Structure H2/H3 headers as questions. “How long does Google Ads suspension typically last?” performs better than “Suspension Timeline Overview.”
Internal linking: Create topical clusters with hub pages linking to supporting content. AI engines follow these structures to understand expertise depth.
Source attribution: Cite sources, include author credentials, link to research. AI engines reward transparent attribution.
Technical performance: Site speed, mobile optimization, and crawlability matter more for AI than traditional search. AI bots are not as powerful as regular SERP crawlers and can’t render JavaScript yet.
Answer density: Include direct, concise answers in the first 100 words, then expand with detail.
Multi-modal optimization: Google Lens processes billions of visual queries monthly. Voice searches are significantly more likely to be questions than text queries. Content with images, diagrams, and video transcripts receives substantially more AI referrals than text-only content. Include alt text, image captions with statistics, and transcribed audio content. AI engines increasingly synthesize answers from multiple content formats & sources. For example, local businesses should optimize their Google Business Profile as AI engines increasingly pull location data from structured business listings.
Citation-ready formatting: Keep primary headers under 60 characters. Include numbers in headlines as AI engines prioritize statistical claims over qualitative statements. Structure H2 headers as complete mini-answers that AI can extract verbatim. Place authority markers (certifications, data volumes, client counts) in the first 100 words where AI engines prioritize source evaluation.
Industry-Specific GEO Performance
GEO adoption and effectiveness vary significantly by sector:
SaaS and fintech lead in AI visibility. Over half of B2B buyers now consult ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Gemini for vendor shortlists before visiting traditional search results. Fintech brands with high topical authority are 2.5x more likely to land in AI citations. AI-native platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity have become the second-largest source for qualified B2B leads at 34%, trailing only social media at 46% and surpassing organic search (10Fold, 2025). Complex products with clear comparison points and decision criteria perform well in AI-generated recommendations.
E-commerce faces mixed results. ChatGPT shopping traffic remains under 1% of total sessions for most retailers but delivers significantly higher conversion rates—Similarweb reports 11.4% for ChatGPT referrals versus 5.3% for organic search. However, a University of Hamburg study analyzing 973 e-commerce sites generating $20 billion in revenue found ChatGPT referrals underperformed most traditional channels. Walmart reports one in five referral clicks now come from ChatGPT. Product queries with clear purchase intent drive better results through conversational interfaces.
Healthcare, legal, and finance face elevated concerns. These regulated industries confront additional challenges around accuracy, liability, and compliance. California enacted Assembly Bill 489 in October 2025 prohibiting AI systems from implying medical advice comes from licensed professionals. Multiple states passed AI healthcare regulations in 2025, with lawsuits targeting insurance companies for AI-driven claim denials. Healthcare providers face complex questions about liability when AI misdiagnoses occur. These industries require extra emphasis on citations, credentials, regulatory compliance, and source verification.
News organizations show high AI adoption. Research reveals 73% of global news organizations have adopted AI technology, with half of newsrooms now working with generative AI tools like ChatGPT (World Association of News Publishers). The Reuters Institute’s 2025 study across six countries found public AI usage jumped from 40% to 61%, with weekly usage nearly doubling from 18% to 34%. However, news publishers face serious traffic concerns…organic traffic to news sites declined from 2.3 billion to 1.7 billion monthly visits while AI-generated news searches surged 212%. ChatGPT referrals to news sites increased 25-fold but cannot offset the massive loss in organic search traffic. News organizations must adapt to zero-click consumption while optimizing for attribution and citation.
B2B content sees selective AI adoption. Detailed technical documentation, comparison pages, and research-backed thought leadership perform well in AI citations. API documentation and integration guides frequently appear in ChatGPT and Copilot responses. Use case pages with real business problem mappings receive strong AI visibility.
However, generic whitepapers and templated content struggle to stand out. Long-form technical content with first-party research and expert insights maintains relevance, as detailed queries still drive clicks to comprehensive sources rather than relying solely on AI summaries.
Measuring GEO Performance
Traditional SEO metrics don’t capture AI visibility. Digital marketing strategies now require new measurement approaches:
AI citation tracking: Monitor how often AI engines mention your brand when users ask relevant questions. Tools like Profound, Superlines, and custom monitoring solutions track brand mentions and citations across ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Share of AI voice: Calculate what percentage of AI responses in your category include your brand versus competitors. This metric replaces traditional search engine market share.
Attribution rate: Measure the fraction of AI answers using your content that explicitly cite your domain. Low attribution despite high content use indicates optimization opportunities.
Zero-click displacement: Track queries where AI provides complete answers without requiring clicks. High displacement with low citation means you’re informing competitors’ visibility rather than your own.
AI-attributed traffic: Segment analytics to identify users arriving from AI-generated results. LLM visitors can convert up to 4.4x better than traditional organic search traffic. Note that most AI referral traffic appears as “Direct” in Google Analytics because AI platforms don’t consistently pass referrer data. Manual tagging and UTM parameters help track AI-sourced sessions accurately.
GEO Tools and Monitoring
Traditional SEO platforms don’t monitor AI powered search engine visibility.
AI-specific platforms: Bear AI tracks citations across 15+ generative engines with pattern analysis. Otterly AI, Profound, Peec, and Semai provide citation monitoring, visibility scoring, and competitive benchmarking specifically for ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Perplexity & other LLMs.
Traditional SEO tools with GEO features: SEMrush added AI Overview tracking and citation analysis in 2025. SurferSEO includes GEO content scoring. Writesonic and Frase.io added AI answer optimization. These platforms reverse-engineer which content structures AI engines prefer.
Implementation approach: Start with one monitoring tool to establish baseline citation rates. Most platforms show measurable visibility changes within weeks of implementing optimization strategies. Citation rates typically improve significantly in the first quarter after optimization.
GEO and SEO Work Together
GEO doesn’t replace SEO but works on top of it. Generative AI engines rely on the same technical foundations: clean site structure, fast load times, mobile optimization, accessible content, proper indexing, and logical information architecture.
SEO optimizes for ranking algorithms. GEO optimizes for synthesis and citation. Strong SEO enables GEO implementation:
- Audit existing content for citation-readiness
- Add statistical support to key claims
- Implement schema markup for structured data
- Restructure content with question-based headers
- Publish case studies with your unique data
- Include authoritative citations
- Build high-quality links to your content
- Publish comparison content (best lists, versus pages) targeting your category
- Monitor AI platform visibility
- Iterate based on citation performance
First-Mover Advantage
AI systems develop citation patterns. Once a platform consistently cites your brand as authoritative, that pattern reinforces across future queries.
Organizations implementing GEO strategies in Q4 2025 and Q1 2026 establish authority signals before competitive saturation. Industry analysis projects that by mid-2026, dominant citation positions will have calcified around early adopters. Delayed implementation creates permanent competitive disadvantage as citation patterns become entrenched.
ChatGPT grew from 100 million weekly users in November 2023 to 800 million in October 2025. AI-sourced traffic increased 527% between January and May 2025. Some enterprise sites now derive over 10% of new customer signups from AI referrals.
Citation inequality compounds quickly. Fewer than 10% of sources cited in ChatGPT, Gemini, and Copilot rank in the top 10 Google organic search results for the same query. Traditional SEO performance doesn’t guarantee AI visibility. Wikipedia demonstrates the scale of this disparity, with significantly higher citation rates in ChatGPT compared to Google AI Overviews. Applied across billions of queries, these differences represent massive visibility gaps.
Implementation Roadmap
Month 1-2: Audit current AI visibility. Use monitoring tools to check how AI platforms represent your brand. Identify consistently cited competitors. Document gaps.
Month 3-4: Optimize high-authority content. Add statistics, authoritative citations, and improved structure to top-performing pages. Implement schema markup. Publish comparison content targeting your category (see Best Lists Strategy).
Month 5-6: Create answer-ready content targeting high-volume AI queries. Use conversational query research to identify what users ask AI systems. Structure content specifically for citation, matching user intent and search intent with direct, comprehensive answers.
Month 7-12: Scale authority building. Develop original research, publish data, earn external citations. Become the referenced source in your category.
Ongoing: Monitor citation performance weekly. Regular tracking identifies shifts in citation patterns and optimization opportunities.
Conclusion
AI-powered search represents a permanent shift in how people find businesses. Traditional search-only strategies leave visibility gaps.
GEO determines whether businesses get cited or ignored when potential customers research through AI tools. Implementation is technical but straightforward. Citation authority compounds as competitors adopt these practices.
For businesses running Google Ads, GEO complements existing strategies. When customers research categories in AI tools before searching Google Ads, citation authority influences whether they search for your brand specifically.
If you need help implementing these strategies, our generative engine optimization services can boost your AI visibility.